Tensorflow feature columns 첫번째 이야기
이장은 feature column에 대해 설명해보도록 하겠습니다. feature column는 raw data와 Estimator사이의 중재자 역할을 한다고 생각하시면 됩니다. feature column은 Estimator가 raw data를 사용할 수 있는 형식으로 변환시키는 다양한 형식을 가지고 있으며 실험을 쉽게 할 수 있게 만들어 줍니다.
우리는 미리 만들어진 Estimator은 DNNClassifier를 사용하여 4가지 feature로 부터 다른 종류의 붓꽃의 종을 예측하는 모델을 학습해 본다고 생각해 봅시다. 이 예제는 tf.feature_column.numeric_column만 사용될 것 입니다.
붓꽃의 종을 예측하는 문제에서는 꽃잎과 꽃받침의 길이을 feature로 사용하기 때문에 numerical(숫자형) feature를 사용하는 것이 적절합니다. 하지만 세상의 많은 문제에서는 non-numerical feature도 많이 사용됩니다.
real-world에서 feature들은 numeric(숫자형) 도 있지만 아닌 경우도 있다.
Input to Deep Neural Network
신경망은 어떻게 계산이 될까요?? 다들 아시겠지만 답은 숫자를 통해서 계산이 됩니다 (사실 컴퓨터는 다 숫자로 표현되어져 있습니다). 신경망은 뉴런은 가중치와 입력데이터에 대해 곱셉과 덧셈을 실시하여 계산됩니다. 그러나 앞에서 말했다 시피 입력 데이터의 형식이 numberical(숫자형)이 아닌 categorical(범주형)의 데이터가 있을수도 있습니다.
예를들어 categorical(범주형) feature인 product_class를 사용한 것을 봅시다.
- kitchenware (주장용품)
- electronics (전자제품)
- sports (스포츠)
ML models은 일반적으로 1이 값이 존재한다는 것을 의미하고 0은 값이 부재한다는 것을 나타내는 간단한 벡터로 categorical(범주형) 값을 나타냅니다 (one-hot vector 라고 이야기 하기도 합니다) product_class를 [0,0,1] 로 표현하면 다음과 같은 의미가 됩니다.
- 0 : kitchenware (표현 X)
- 0 : electronics (표현 X)
- 1 : sports (표현 O)
스포츠용품을 선택하였다.
즉, raw data가 numerical(숫자형) 이거나 categorical(범주형) 데이터 일지는 알 수가 없지만 ML model에서는 모든 feature 들을 숫자로 기억하고 있어야 됩니다.
Feature Columns
아래의 그림에서 알수 있듯이 Estimator의 feature_columns를 통하여 모델에 대한 입력을 지정합니다.
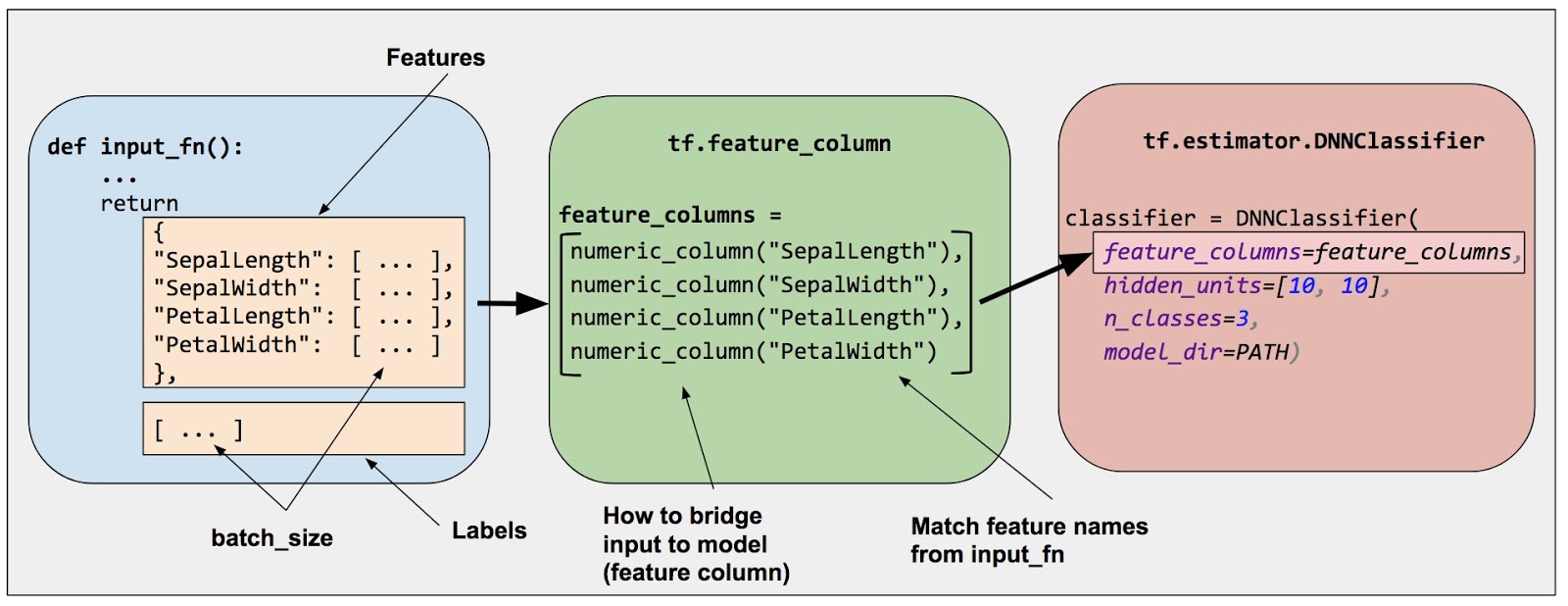
feater columns은 모델에 필요한 데이터와 raw 데이터를 연결하는 역할을 합니다.
feature_columns를 작성하려면 tf.feature_column모듈에서 메서드들을 호출하면 됩니다. 이 장에서는 아래 그램에서 보듯이 9개의 함수 모두 양 카테코리에서 상속한 bucketized_column을 제외하고 Categorical Column 또는 Dense Column 객체를 반환합니다.
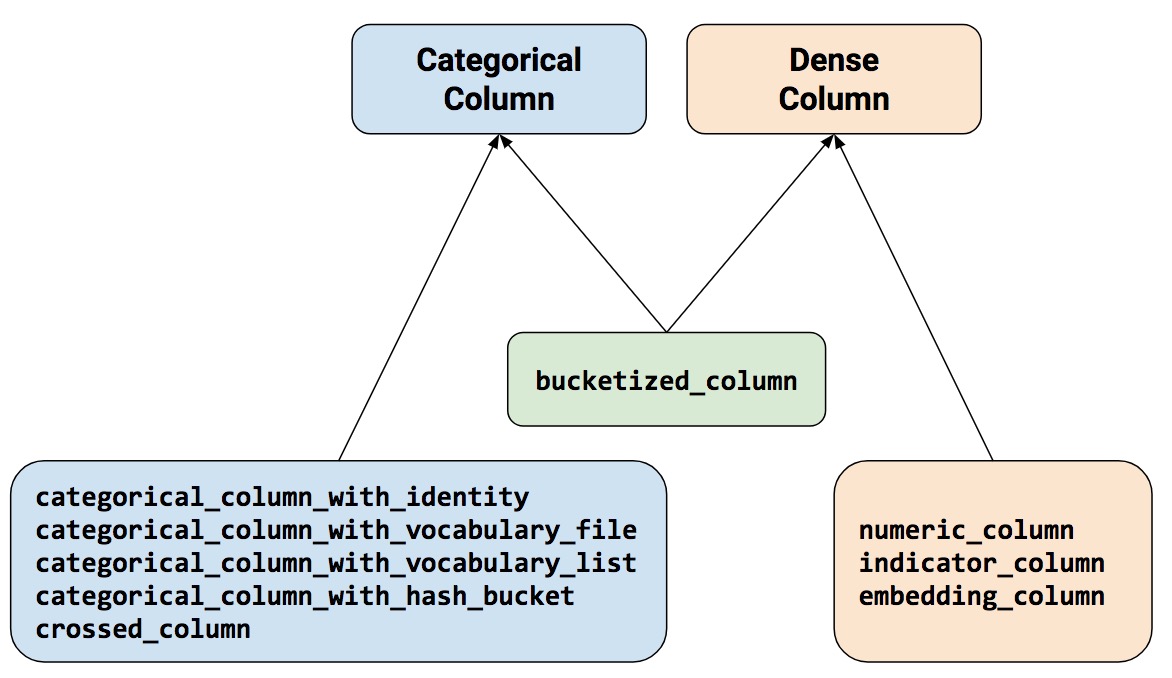
feature_columns은 크게 2개의 객체로 구성되어져 있고 하나의 하이브리드 범주가 있습니다.
이제 자세히 설명을 시작해 보겠습니다.
Numeric column
iris 분류기는 입력 feature들에 대해 tf.feature_column.numeric_column(숫자형) 함수를 호출합니다.
- SepalLength
- SepalWidth
- PetalLength
- PetalWidth
tf.feature_column.numeric_column 인수없이 호출하면 기본 데이터 유형 (tf.float32)을 모델에 대한 입력으로 사용하여 숫자 값을 지정할 수 합니다.
# Defaults to a tf.float32 scaler
numeric_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key="SepalLength")
dtype에 인수를 지정해 데이터 유형을 바꿔줄 수도 있습니다.
# Defaults to a tf.float32 scaler
numeric_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key="SepalLength",
dtype=tf.float64)
기본적으로 tf.feature_column.numeric_column는 scaler(단일값) 만들어줍니다. 하지만 만약 shape인수를 사용하여 다른 모양으로 만들어 줄수 있습니다.
# Represent a 10-element vector in which each cell contains a tf.float32.
vector_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key="Bowling",
shape=10)
# Represent a 10x5 matrix in which each cell contains a tf.float32.
matrix_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key="MyMatrix",
shape=[10,5])
Bucketized column
종종 모델에 숫자를 직접 입력하는 대신 숫자 범위에 따라 다른 카테고리로 값을 분할하는 것이 좋을때가 있습니다. 이런 기능을 사용하기 위해서 Bucketized column을 사용하면 좋습니다. 예를들어 주택이 건설된 연도를 나타내는 raw data가 있다고 가정합시다. 이 데이터는 단순히 scalar(숫자)로 나타내지 않고 네 개의 bucket으로 나눌 수 있습니다.
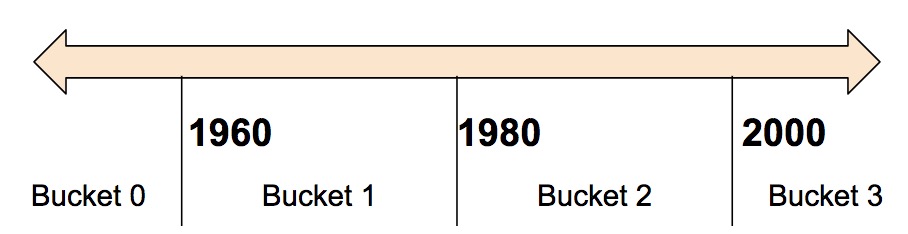
모델은 buckets을 다음과 같이 나타냅니다.
| Data Range | Represented as… |
|---|---|
| < 1960 | [1, 0, 0, 0] |
| >= 1960 but < 1980 | [0, 1, 0, 0] |
| >= 1980 but < 2000 | [0, 0, 1, 0] |
| > 2000 | [0, 0, 0, 1] |
왜 이런식으로 numeric(숫자) 데이터를 categorical(범주형) 데이터로 분리하는 것일까요?? 위와 같이 buckets화를 하면 numeric(숫자)데이터를 네 요소의 벡터로 나눠지게 되어 모델안으로 4개의 데이터가 입력으로 주어집니다. 따라서 모델은 1개가 아닌 4개에 개별 가중치를 학습할 수 있게 되고 4개의 가중치는 1개의 가중치보다 더 표현력이 풍부한 모델을 만들 수 있습니다. 더 중요한 것은 buckets화는 feature중 하나는 1로 설정되고 나머지 요소는 0으로 설정되기 때문에 다른 연도의 범주를 명확하게 구분할 수 있습니다. 만약 숫자(년도)를 입력으로 사용하면 모델은 선형관계만 배울수 있습니다. 따라서 bucket은 학습에 사용할 수 있는 추가 유연성을 제공합니다.
아래 코드를 통해 Bucketized column를 어떤식으로 사용하는지 알아보자
# First, convert the raw input to a numeric column.
numeric_feature_column = tf.feature_column.numeric_column("Year")
# Then, bucketize the numeric column on the years 1960, 1980, and 2000.
bucketized_feature_column = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(
source_column = numeric_feature_column,
boundaries = [1960, 1980, 2000]
3가지 요소로 boundaries를 지정하면 4가지 요소의 bucket vector가 만들어집니다.
Categorical identity column
categorical identity columns는 bucketized columns의 특수한 경우라고 보시면 됩니다. 기존의 bucketized columns은 값의 범위를 나타내지만 categorical identity columns은 각 bucket은 단일 고유한 정수를 나타냅니다.
예를들어 [0, 4)의 범위를 가지는 정수범위를 나타내고 싶다고 가정합시다. 그러면 정수 0, 1, 2, 3으로 나타내질껍니다. 이떄 categorical identity column을 적용하면 아래와 같이 나타내지게 됩니다.
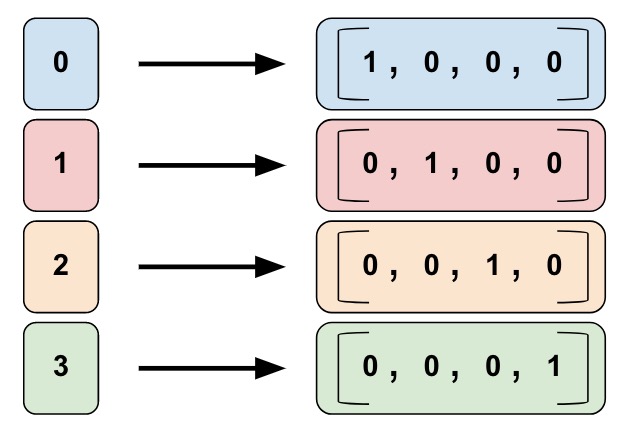
categorical 별로 id를 mapping한 것입니다. one-hot-encoding으로 불려지기도 합니다.
bucketized columns과 마찬가지로 categorical identity columns는 각 클래스에 대해 별도의 가중치를 학습할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 문자열을 사용하여 product_class를 나타내는 대신에 각 클래스의 고유한 정수값으로 나타내 보면 아래와 같을 것입니다.
- 0 = “kitchenware”
- 1 = “electronics”
- 2 = “sport”
categorical identity columns을 구현하려면 tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity를 사용하면 된다.
# Create categorical output for an integer feature named "my_feature_b",
# The values of my_feature_b must be >= 0 and < num_buckets
identity_feature_column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(
key='my_feature_b',
num_buckets=4) # Values [0, 4)
# In order for the preceding call to work, the input_fn() must return
# a dictionary containing 'my_feature_b' as a key. Furthermore, the values
# assigned to 'my_feature_b' must belong to the set [0, 4).
def input_fn():
...
return ({ 'my_feature_a':[7, 9, 5, 2], 'my_feature_b':[3, 1, 2, 2] },
[Label_values])
Categorical vocabulary column
모델안에 input 데이터를 넣을때 string형으로 넣을수는 없습니다. string 데이터를 numeric(숫자형) 또는 categorical(범주형)으로 바꿔줘야됩니다. categorical vocabularay column는 string 데이터를 ont-hot vector로 표현하는 좋은 방법을 제공합니다.
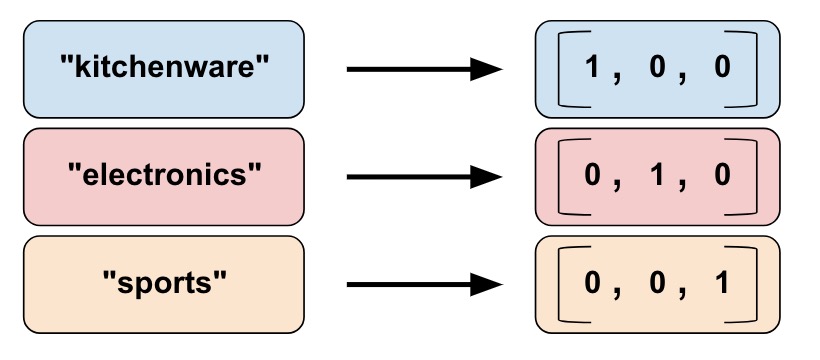
string 값을 vocabularay column 으로 mapping 시켰습니다.
보시다시피 categorical vocabularay columns은 categorical identity columns의 열거형 버전중 하나하는 것을 아실 수가 있습니다.
Tensorflow 에서는 두가지 종류의 categorical vocabularayn columns 함수를 제공합니다.
tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_listtf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file
tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list은 어휘목록을 기반으로 string 데이터를 integer 데이터로 매핑시킵니다.
예를들어
# Given input "feature_name_from_input_fn" which is a string,
# create a categorical feature by mapping the input to one of
# the elements in the vocabulary list.
vocabulary_feature_column =
tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(
key="a feature returned by input_fn()",
vocabulary_list=["kitchenware", "electronics", "sports"])
tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file은 어휘목록을 기반으로 string 데이터를 integer 데이터로 매핑시킵니다.
앞의 함수는 간단하지만 중요한 단점이 있습니다. 어휘 목록이 길면 입력이 너무 많아져 사용의 불편함이 있을 수 있습니다. tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file를
# Given input "feature_name_from_input_fn" which is a string,
# create a categorical feature to our model by mapping the input to one of
# the elements in the vocabulary file
vocabulary_feature_column =
tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
key="a feature returned by input_fn()",
vocabulary_file="product_class.txt",
vocabulary_size=3)
product_class.txt를 작성할 시 각 어휘에 대해 한 줄씩 작성하시면 됩니다.
# product_class.txt 파일
kitchenware
electronics
sport
Hashed Column
지금까지 우리는 작은개수의 categories 만으로만 작업했습니다. 예를들어 product_class 예제에서는 3개의 categories 만 사용합니다. 그러나 종종 categories 의 수가 너무 많아서 각 word나 integer에 대해 개별 categories를 가질수가 없을수가 없을수도 있습니다. 왜냐하면 너무 많은 메모리를 사용하게 되기 때문입니다. 이경우 대신에 질문을 돌려서 질문을 할 수 있습니다. “입력할 categories의 수는 몇 가지 입니까?”
